LinkedList(연결 리스트)
LinkedList
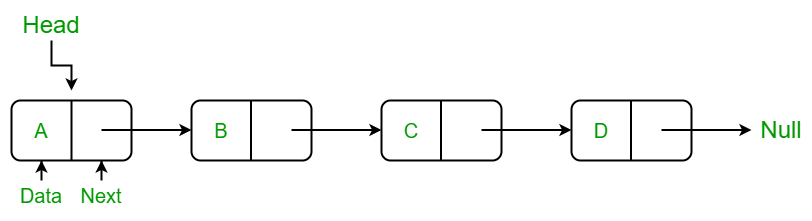
- Data를 감싼 node를 pointer로 연결하여 관리하는 자료구조이다.
- Array와 동일하게 elemnt가 일렬로 나열되어 있는 선형 자료구조이다.
- node(노드) : Data 저장 단위로 Data 값과 pointer(next)로 구성
- pointer(포인터) : 각 node 안에서 다음 혹은 이전의 node와 연결 정보(Memory 주소)를 가지고 있는 공간
Java로 구현해보기
- node 클래스 구현
public class Node<T> {
T data;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node라는 클래스에 node의 data와 다음 node를 가르키는 pointer인 next를 선언했다.
- node 인스턴스 간 연결
Node<Integer> node1 = new Node<Integer>(1);
Node<Integer> node2 = new Node<Integer>(2);
node1.next = node2;
Node<Integer> head = node1;
node간 연결을 위해 node1과 node2라는 객체를 생성한다. node1의 pointer 값이 node2를 가르키도록 한다. 이 때, 어떤 node가 맨 앞인지 모르기때문에, head라는 객체를 통해 가장 첫 노드를 가르키도록 한다.
- Data 추가하기 (SingleLinkedList 기준)
public class LnikedList<T> { public Node<T> head = null; public class Node<T> { T data; Node<T> next = null; public Node(T data) { this.data = data; } } public void addNode(T data) { if(head == null) { head == new Node<T>(data); } else { Node<T> node = this.head; while (node.next!=null) { node = node.next; } node.next = new Node<T>(data); } } }최초 Node에는 head에 아무것도 없기 때문에 null로 선언한다. addNode 메서드에서 head==null(첫 node)라면 head에 새로운 node를 추가시킨다. 이 후, node의 next가 null이 아니라면, 다음 node가 있다는 것을 의미하기 때문에, 현재 node를 다음 node를 가르키도록 한다.
- data 출력
public void print() {
if (head != null) {
Node<T> node = this.head;
System.out.println(node.data);
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
}
// main 메서
SingleLinkedList<Integer> MyLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList<Integer>();
MyLinkedList.addNode(1);
MyLinkedList.addNode(2);
MyLinkedList.addNode(3);
MyLinkedList.print();
// 1
// 2
// 3
- 특정 위치 data 추가
public Node<T> search(T data) {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
} else {
Node<T> node = this.head;
while(node != null) {
if (node.data == data) {
return node;
} else {
node = node.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public void addNodeInside(T data, T isData) {
Node<T> searchedNode = this.search(isData);
if (searchedNode == null) {
this.addNode(data);
} else {
Node<T> nextNode = searchedNode.next;
searchedNode.next = new Node<T>(data);
searchedNode.next.next = nextNode;
}
}
- 특정 node 삭제
public boolean deleteNode(T isData) { if (this.head == null) { return false; } else { Node<T> node = this.head; if (node.data == isData) { this.head = this.head.next; return true; } else { while (node.next != null) { if (node.next.data == isData) { node.next = node.next.next; return true; } node = node.next; } return false; } } } - 결과 출력
// main 메서드 SingleLinkedList<Integer> list = new SingleLinkedList<Integer>(); list.addNode(1); // 1 list.addNode(2); // 1, 2 list.addNode(3); // 1, 2, 3 list.addNodeInside(5 ,1); // 1, 5, 2, 3 list.deleteNode(5); // 1, 2, 3 list.print(); // 1, 2, 3
특징
data 공간을 미리 할당(정적)하는 Array와 달리 data 공간을 미리 할당하지 않아도 된다(동적). 하지만 연결(link)를 위한 별도 data 공간(pointer)가 필요하므로 저장공간의 효율이 높지 않으며, 연결 정보를 찾는 시간이 필요하여 접근 속도가 느리다. 또한 중간 data삽입(혹은 삭제)시 앞, 뒤 data의 연결을 재구성해야 하는 부가적 작업이 필요하다.
–
LinkedList의 시간복잡도 (Single-Linkedlist 기준)
- 접근
x번 index에 있는 node에 접근 시, head에서 다음 node로 x번 가면되는데, 이 때 시간 복잡도는 O(n)이다.
- 탐색
가장 앞 node(head)부터 다음 node를 하나씩 탐색하여 원하는 data를 찾는다.(선형 탐색) 이 때, data가 없거나 찾으려는 data가 가장 끝 노드에 있는 최악의 경우 n개의 node를 모두 탐색해야한다. 따라서 시간 복잡도는 O(n)이 된다.
- 삽입 및 삭제
data를 삽입하거나 삭제하는 행위 자체의 시간 복잡도는 O(1)이지만, data의 위치가 head가 아닌 x번째라고 한다면 순차적으로 탐색하여 해당 위치까지 가게되는데 이 때의 시간 복잡도는 O(n)이 된다.
다양한 구조의 LinkedList
-
Singly-Linkedlist(단일 연결 리스트) : 상단의 예
-
Doubly-Linkedlist(이중 연결 리스트)

다음 node를 가르키는 next에 이전 node(backwars 혹은 prev)를 추가한 구조이다.
- Circular-Linkedlist(원형 연결 리스트)

마지막 pointer가 첫 node(head)를 가르키는 구조이다.
참고자료
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DzGnME1jIwY&ab_channel=%EC%97%94%EC%A7%80%EB%8B%88%EC%96%B4%EB%8C%80%ED%95%9C%EB%AF%BC%EA%B5%AD
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list
- https://opentutorials.org/module/1335/8821
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-linked-list/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list