Hash table(해쉬 테이블)
Hash table (해쉬 테이블)
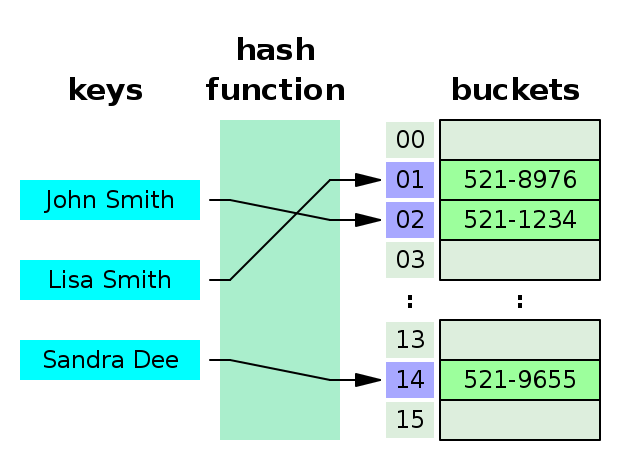
- Hash table은 Key(키)에 Data(데이터)를 Mapping할 수 있는 데이터 구조이다.
- Hash fucntion(해쉬 함수) 를 통해, 배열에 Key에 대한 Data를 저장할 수 있는 주소(index)를 계산한다.
- Key를 통해 Data가 저장되어 있는 주소를 알 수 있다. -> 저장 및 탐색 속도가 빠르다.
- 이 때, 특별한 알고리즘을 이용하여(하단의 설명의 예로 division method) 저장할 data와 연관된 고유한 숫자를 만들어 index로 사용한다.
- 용어
- Hash : 임의 값을 고정 길이로 변환하는 것
- Hash table : key값의 연산에 의해 직접 접근이 가능한 data 구조
- Hash function(hash method) : key에 대해 산술 연산을 통한 data 위치를 찾을 수 있는 함수
- Hash code : Hash function에 의해 반환된 data의 고유 숫자
- Hash Value(Address) : Hash function를 통해 return된 고정 길이값
- Slot(buckets) : 한 개의 data를 저장할 수 있는 공간
Java로 구현한 Hashtable
- Hash table 구현
public class HashEx1 {
public Slot[] hashtable;
public HashEx1(int size) {
this.hashtable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot {
String value;
Slot(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
}
각 slot에 String value를 담은 Array(Slot[])를 담도록 했다.
- Hash function 추가
public class HashEx1 {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public HashEx1(int size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot {
String value;
Slot(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunction(String key) {
return (int)(key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
}
HashEx1의 경우 Division method를 통해 문자열 Key 문자열의 앞 글자(charAt(0))를 숫자로 변환하여 Key에 대한 index 번호(주소)를 계산하도록 적용했다.
- Data 저장
public boolean saveData(String key, String value) {
int address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(value);
}
return true;
}
}
if문에서 현재 hashtable에 해당 index(address)가 null이 아니라면 (data가 이미 한 번 저장된 경우) value를 가르키도록 하고,
else문은 해당 slot이 만들어지지 않은 경우로 해당 index(address)에 slot 객체를 하나 생성한다.
- Key에 대한 Data 가져오기
public String getData(String key) {
int address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
return this.hashTable[address].value;
} else {
return null;
}
}
key를 넣게되면 address를 hashFunction으로 가져오게 하고, 해당 address에 null이 아니라면(Slot이 있는 경우) 객체가 없다면(Slot이 없는 경우) null을 return하도록 한다.
- main 메서드에서 실행
HashEx1 hs = new HashEx1(10);
hs.saveData("Rome", "123");
hs.saveData("Seoul", "456");
hs.getData("Seoul"); // 456
Hash table의 특징
- data 저장 및 읽기 속도가 빠르다. (검색속도가 빠름)
- 이 때문에 검색이 많이 필요한 경우, 저장/삭제가 빈번하고 중복확인이 쉬운 캐쉬 구현 시 사용된다.
- Key에 대한 data가 있는지 중복 확인이 쉽다.
- 특정 data가 저장되는 index는 고유한 위치이기 때문에, 삽입 연산 시 다른 data가 끼어들거나, 삭제 시 다른 data로 채울 필요가 없어 연산에서 추가적인 비용이 없도록 만들어진 구조다.
- 여러 Key에 대한 address가 동일하다면 충돌을 해결하기 위한 다른 구조가 필요하다.
Collision(충돌) 해결 알고리즘
- Collision(충돌)
HashEx1 hs = new HashEx1(10);
hs.saveData("Rome", "123");
hs.saveData("Seoul", "456");
hs.saveData("RiodeJaneiro", "789");
hs.getData("Rome"); // 789
예시를 살펴보자.
각 key에 data를 저장하고 Rome의 data를 조회했을 때, 기댓값은 123이지만 789라는 data값을 얻게 되었다. 이는 division method를 통해 key값의 첫 글자(위의 경우는 R)를 기준으로 slot에 address값을 넣었기 때문이다.
이처럼 서로 다른 키(key)가 같은 해시(hash)가 되는 경우를 해시 충돌이라고 하는데 이를 해결하기 위한 몇 가지 알고리즘을 살펴보자.
- Chaining

Open Hashing(개방 해싱) 방법 중 하나로 Hash table 저장공간 외의 공간을 활용하는 방법으로, Collision이 일어나면 LinkedList를 사용해 LinkedList로 data를 투가로 뒤에 연결시켜 저장하는 방법이다.
public class HashEx2 {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public HashEx2(int size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot {
String key;
String value;
Slot next;
Slot(String key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = null; // pointer 값인 next 추가
}
}
public int hashFunction(String key) {
return (int) (key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value) {
int address = this.hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
Slot findSlot = this.hashTable[address];
Slot prevSlot = this.hashTable[address];
while (findSlot != null) { // Linkedlist를 순회
if (findSlot.key == key) {
findSlot.value = value;
return true;
} else {
prevSlot = findSlot;
findSlot = findSlot.next; // Collision 발생 시, pointer가 가르키는 slot으로
}
}
prevSlot.next = new Slot(key, value);
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String getData(String key) {
Integer address = this.hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
Slot findSlot = this.hashTable[address];
while (findSlot != null) {
if (findSlot.key == key) {
return findSlot.value;
} else {
findSlot = findSlot.next;
}
}
return null;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
// main 메서드에서 실행
HashEx2 hs = new HashEx2(10);
hs.saveData("Rome", "123");
hs.saveData("Seoul", "456");
hs.saveData("RiodeJaneiro", "789");
hs.getData("Rome"); // 123
- Linear Probing

Open Addressing(개방 주소 지정) 방법 중 하나인 Linear Probing은 Close Hashing(폐쇄 해싱)의 하나로 Hash table 저장공간 안에서 충돌 문제를 해결하는 방법으로, Collision 발생 시 해당 Hash address의 다음 address부터 맨 처음 나오는 빈 공간에 저장하는 방법이다.
public class HashEx3 {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public HashEx3(Integer size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot {
String key;
String value;
Slot(String key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunction(String key) {
return (int) (key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value) {
Integer address = this.hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) { // slot이 있는 경우
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key) {
this.hashTable[address].value = value; // value를 update
return true;
} else {
int currentAddress = address + 1;
while (this.hashTable[currentAddress] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[currentAddress].key == key) { // hash table 현재 address의 값이 내가 찾는 key인지 확인
this.hashTable[currentAddress].value = value; // 현재 address의 값을 update
return true;
} else {
currentAddress++;
if (currentAddress >= this.hashTable.length) { // array의 size를 넘어선다면 false를 return
return false;
}
}
}
this.hashTable[currentAddress] = new Slot(key, value);
return true;
}
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String getData(String key) {
int address = this.hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key) {
return this.hashTable[address].value;
} else {
int currentAddress = address; // 수정
while (this.hashTable[currentAddress] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[currentAddress].key == key) {
return this.hashTable[currentAddress].value;
} else {
currentAddress++;
if (currentAddress >= this.hashTable.length) {
return null;
}
}
}
return null;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
// main 메서드에서 실행
HashEx3 hs = new HashEx3(10);
hs.saveData("Rome", "123");
hs.saveData("Seoul", "456");
hs.saveData("RiodeJaneiro", "789");
hs.getData("Rome"); // 123
else 구문에서 key에 해당하는 address가 가장 마지막 slot일 경우, this.hashTable[address + 1] 에 해당하는 배열은 없기 때문에, 예외 케이스에서도 동작하도록 currAddress 는 address만 대입했다.
이러한 linear probing 방법은 사용하면 data들이 특정 위치에만 밀집하는 clustering 문제가 발생할 수 있어 n^2를 건너뛰어 빈 공간(Slot)을 찾아가는 quadratic probing을 사용하기도 한다.
- 해시 버킷 동적 확장(Resize)
Hash Bucket의 개수가 적다면 메모리 사용을 아낄 수 있지만 해시 충돌로 인해 성능 상 손실이 발생한다. 그래서 HashMap은 key-value 쌍 데이터 개수가 일정 개수 이상이 되면 해시 버킷의 개수를 두 배로 늘린다. 이렇게 늘리면 Hash Collision으로 인한 성능 손실 문제를 어느 정도 해결할 수 있다. Hash Bucket을 두 배로 확장하는 임계점은 현재 데이터 개수가 해시 버킷의 개수의 75%가 될 때이다. 이 0.75라는 수는 load factor라고 한다.
Hash의 시간 복잡도
Collision이 없는 일반적인 경우 시간 복잡도는 O(1) 이며, 최악(Collision이 모두 발생)하는 경우 시간 복잡도는 O(n) 이 된다. Hash table의 경우 일반적인 경우를 기대하고 작성한다.
Collision이 많아 질수록 탐색에 필요한 Time Complexity가 O(1)에서 O(n)에 가까워지기 때문에, 상황에 따라 상단의 예와 같은 Hash function 및 방법을 이용하여 Hash table 성능 향상을 가져올 수 있다.
참고자료
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table - Hashtable 이미지
- https://www.fun-coding.org/Chapter09-hashtable-live.html#gsc.tab=0 - 용어 설명
- https://youtu.be/Vi0hauJemxA - Hash 설명
- https://blog.naver.com/PostView.naver?isHttpsRedirect=true&blogId=cestlavie_01&logNo=220932263930 - division method
- https://github.com/JaeYeopHan/Interview_Question_for_Beginner/tree/master/DataStructure#hash-table
- https://ai-rtistic.com/2022/01/29/data-structure-hash/ - chaining, Linear probing